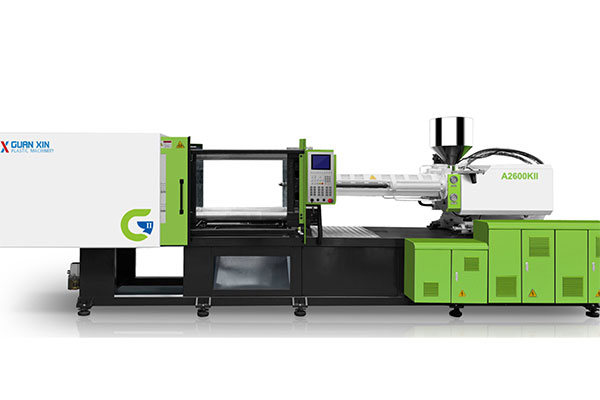
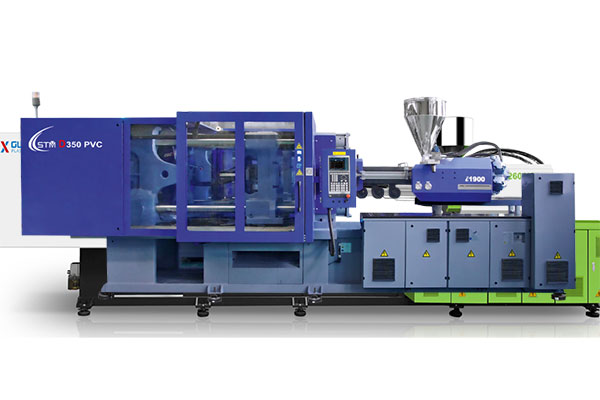
Plastic injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes for producing plastic parts in large volumes. Central to this process is the injection molding machine, a piece of equipment that melts plastic pellets and injects them into a mold to form the desired shape. With applications ranging from automotive and consumer electronics to medical devices and packaging, injection molding is essential to modern manufacturing.
Introduzione alle prestazioni del prodotto
The equipment used in plastic injection molding plays a pivotal role in determining the efficiency, precision, and scalability of the production process. This article provides a detailed introduction to injection molding machines, covering their components, types, operating principles, auxiliary systems, and current trends in technology.
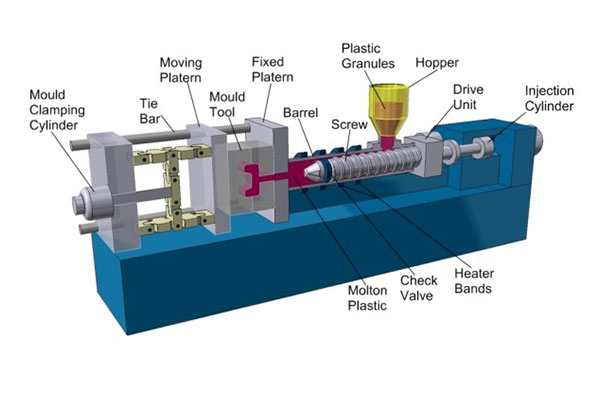
plastic injection molding equipment
2. Overview of the Injection Molding Process
Plastic injection molding is a cyclical manufacturing process that involves the following main steps:
-
Material Feeding: Thermoplastic pellets or granules are fed into a hopper.
-
Melting and Plasticizing: The plastic is heated and melted in the barrel.
-
Injection: The molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity.
-
Cooling and Solidifying: The material cools and takes the shape of the mold.
-
Mold Opening and Ejection: The mold opens and the part is ejected.
-
Repeat Cycle: The cycle restarts for the next part.
This process requires high precision and efficiency, which are achieved through a combination of mechanical, hydraulic, electrical, and thermal systems integrated within the injection molding machine.
3. Core Components of Plastic Injection Molding Equipment
3.1 Injection Unit
The injection unit is responsible for melting and injecting the plastic into the mold. It consists of:
-
Hopper: Feeds raw plastic material (granules or pellets) into the barrel.
-
Barrel: Heated tube where plastic is melted.
-
Screw: Rotates and moves axially to melt, mix, and inject the plastic.
-
Heater Bands: Electric heaters wrapped around the barrel to maintain precise temperature.
-
Nozzle: Directs molten plastic into the mold.
3.2 Clamping Unit
This unit holds the mold and provides the force necessary to keep it closed during injection.
-
Clamping Mechanism: Usually hydraulic, toggle, or electric.
-
Movable and Fixed Platens: Hold the two halves of the mold.
-
Tie Bars: Ensure alignment and withstand the clamping force.
-
Ejection System: Pushes the molded part out after cooling.
3.3 Control System
Modern machines are equipped with computerized control systems (HMI - Human Machine Interface) to manage:
-
Temperature
-
Pressure
-
Injection speed
-
Timing sequences
-
Alarm systems
-
Data logging and diagnostics
4. Types of Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding equipment can be categorized based on the type of drive system used:
4.1 Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
-
Most traditional and widely used.
-
Utilize hydraulic cylinders for clamping and injection.
-
Offer high clamping force and durability.
-
Suitable for large parts and high-pressure applications.
-
Tend to consume more energy.
4.2 Electric Injection Molding Machines
-
Use servo motors for all movements.
-
High precision and energy efficiency.
-
Clean operation—ideal for medical and food-grade applications.
-
Higher initial cost but lower operational cost.
4.3 Hybrid Injection Molding Machines
-
Combine hydraulic and electric systems.
-
Offer a balance between cost, speed, and energy efficiency.
-
Often used in mid-range applications.
5. Advanced Injection Molding Technologies
5.1 Two-Shot or Multi-Shot Molding
Involves injecting two or more materials in a single cycle. Used for parts with multiple colors or materials.
5.2 Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
Uses gas (usually nitrogen) to push the plastic into the mold. Helps create hollow sections and reduces weight and material use.
5.3 Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Molding
Specialized process for medical and electronic components. Requires dedicated equipment that handles two-part liquid silicone.
5.4 Micro Injection Molding
Used for producing ultra-small parts in the medical and electronics industries. Requires high-precision equipment.
5.5 Co-Injection Molding
Enables molding of multi-layer parts with different materials in the core and skin. Used in automotive and packaging.
6. Auxiliary Equipment in Injection Molding
Besides the main injection molding machine, the production line typically includes:
6.1 Mold Temperature Controller
Maintains the mold at the desired temperature to ensure consistent part quality.
6.2 Chillers
Used to cool down the mold quickly to shorten cycle time.
6.3 Material Dryer
Removes moisture from plastic pellets before processing to prevent defects like bubbles or weak weld lines.
6.4 Hopper Loader
Automatically feeds material from storage bins into the hopper.
6.5 Robots and Automation
Used for part removal, quality inspection, and packaging. Enhances efficiency and reduces labor costs.
7. Key Performance Metrics of Injection Molding Equipment
Understanding these metrics is critical to selecting and optimizing equipment:
-
Clamping Force (measured in tons): Determines the size and type of mold that can be used.
-
Injection Pressure: Affects the ability to fill the mold.
-
Shot Size: Maximum volume of material injected per cycle.
-
Cycle Time: Duration of one full molding cycle.
-
Energy Consumption: Varies significantly between machine types.
-
Precision and Repeatability: Essential for high-quality production.
8. Applications of Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding machines are used across diverse industries, including:
8.1 Automotive
-
Bumpers, dashboards, light housings
-
Emphasis on durability, size, and surface finish
8.2 Electronics
-
Housings for phones, laptops, connectors
-
Focus on precision and aesthetics
8.3 Medical
-
Syringes, surgical instruments, diagnostic devices
-
Must comply with strict cleanliness and safety standards
8.4 Packaging
-
Bottle caps, containers, closures
-
High-speed machines preferred
8.5 Consumer Goods
-
Toys, kitchenware, household items
-
Variety in material and finish requirements
9. Leading Manufacturers of Injection Molding Equipment
Some globally recognized manufacturers include:
-
Arburg (Germany)
-
ENGEL (Austria)
-
Haitian International (China)
-
Milacron (USA)
-
Sumitomo Demag (Japan/Germany)
-
Nissei Plastic Industrial (Japan)
-
KraussMaffei (Germany)
These companies offer a range of machines from micro to large-format injection molders with innovative features.
10. Recent Innovations and Industry Trends
10.1 Industry 4.0 Integration
-
Real-time monitoring, data analytics, predictive maintenance
-
Smart sensors and IoT integration for remote diagnostics
10.2 Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
-
All-electric machines and energy recovery systems
-
Use of bioplastics and recycled materials
10.3 Advanced Materials Compatibility
-
Machines designed for composite materials, LSR, and high-temperature plastics
10.4 Additive Manufacturing Integration
-
Combining 3D printing with injection molding for prototyping and hybrid parts
11. Considerations When Choosing Injection Molding Equipment
Choosing the right equipment involves evaluating several factors:
-
Product Size and Complexity
-
Material Requirements
-
Production Volume
-
Precision and Tolerance Needs
-
Automation Level
-
Budget and Operating Costs
-
Conformità normativa (especially for medical and food applications)
12. Maintenance and Safety
Proper maintenance is critical for machine longevity and safety:
-
Routine Checks: Screws, heaters, hydraulic systems, sensors
-
Lubrication and Cleaning: Prevents wear and material contamination
-
Safety Systems: Emergency stops, safety gates, interlocks
-
Operator Training: Minimizes human error and improves productivity
Altri prodotti correlati






