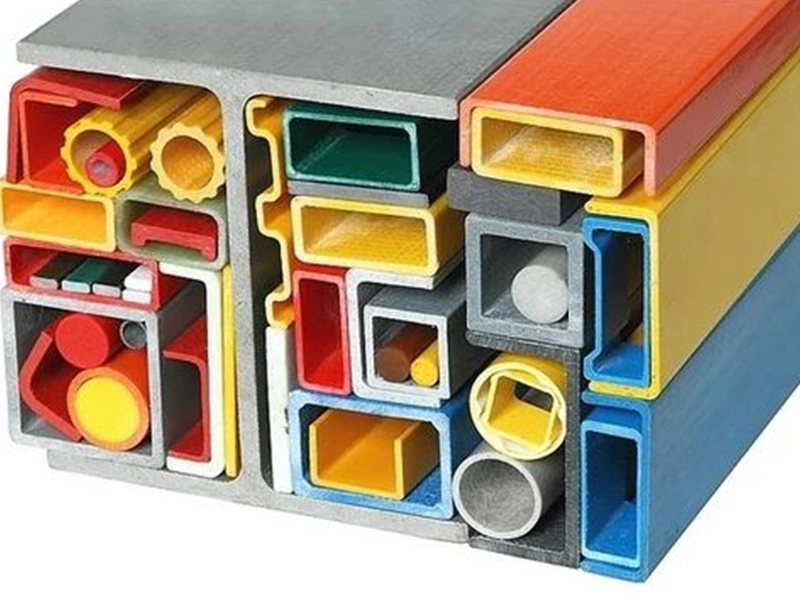
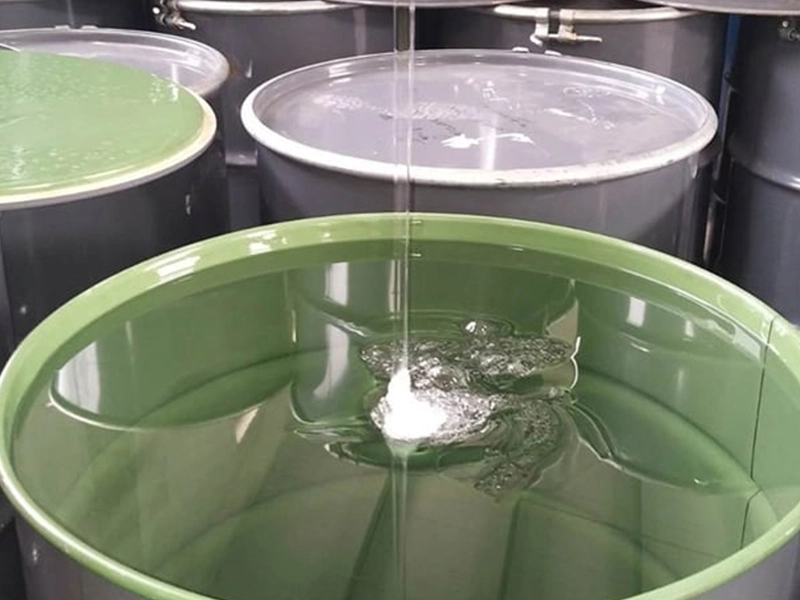
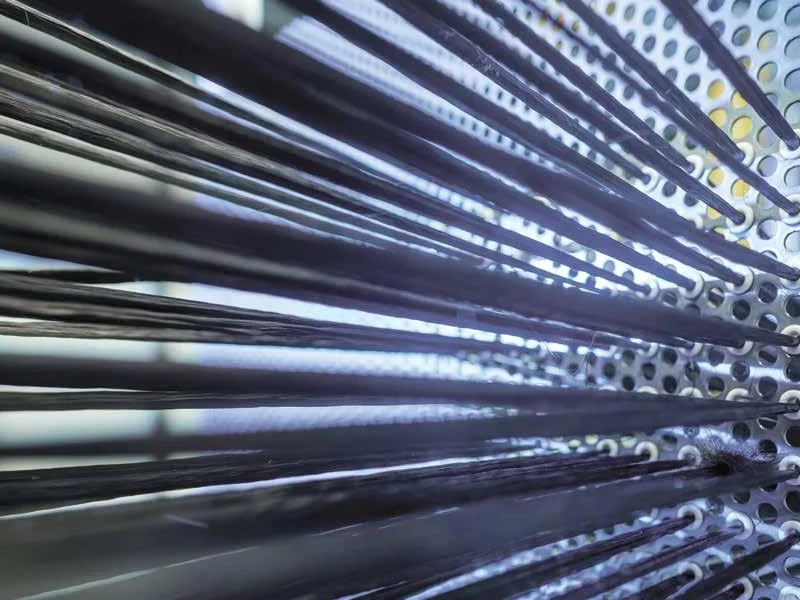
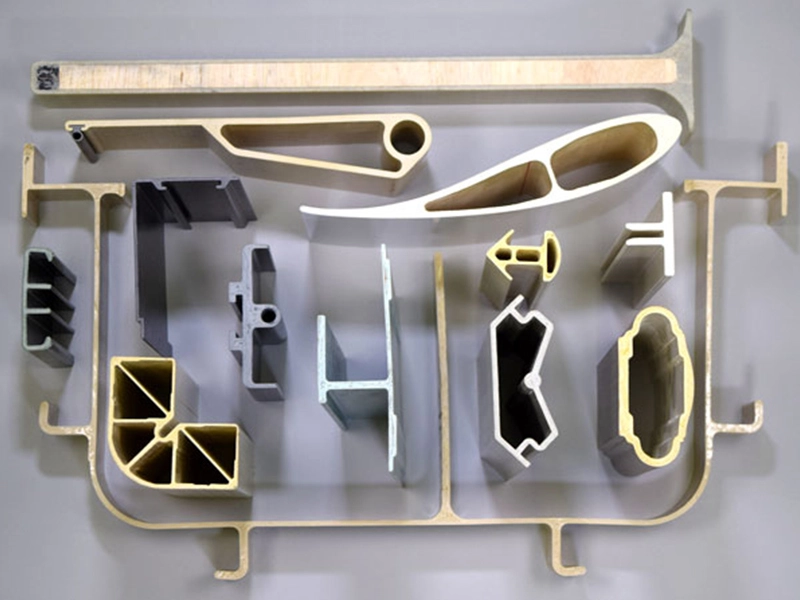
Pultrusion is used to form composites into long, consistent shapes like rods or bars.
Product performance introduction
Pultrusion Resin
Series :
Unsaturated Polyester Resin >application
Pultrusion is used to form composites into long, consistent shapes like rods or bars.
Product Name :
Pultrusion Resin
FAQ
Q :
What are the common types of resins used in pultrusion?
A :
The most common resins used in pultrusion are thermoset resins, such as polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy. These resins provide the necessary mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability required for pultruded composites.
Q :
What are the key properties of pultrusion resins?
A :
Mechanical properties: Tensile strength, flexural strength, and modulus of elasticity to support the structural integrity of the pultruded parts. Chemical resistance: Ability to withstand exposure to various chemicals, solvents, and environmental conditions. Thermal stability: Resistance to high temperatures and thermal cycling without degradation. Viscosity: Appropriate viscosity for efficient impregnation of the reinforcement fibers during the pultrusion process. Curing characteristics: Suitable curing time and exothermic behavior for the pultrusion process.
Q :
How do pultrusion resins differ from other composite resins?
A :
Pultrusion resins are typically formulated to have a lower viscosity compared to resins used in other composite manufacturing processes, such as hand layup or infusion. This lower viscosity allows for better fiber wet-out and impregnation during the continuous pultrusion process. Pultrusion resins also often have faster curing characteristics to enable the continuous production of pultruded parts.
Q :
What are the common reinforcement materials used with pultrusion resins?
A :
The most common reinforcement materials used in pultrusion are continuous glass fibers, carbon fibers, and aramid fibers. These fibers provide the necessary strength and stiffness to the pultruded composite parts.
Q :
How are pultrusion resins formulated and customized?
A :
Pultrusion resin formulations are typically developed by resin manufacturers in collaboration with pultrusion manufacturers. The resin formulation is tailored to meet the specific performance requirements, processing characteristics, and end-use applications of the pultruded products. Additives, such as fillers, thixotropic agents, and UV stabilizers, may be incorporated into the resin formulation to enhance specific properties or processing characteristics.
Q :
What are the key considerations in selecting a pultrusion resin?
A :
Mechanical properties: Tensile, flexural, and compressive strength, as well as stiffness, to meet the structural requirements of the application. Chemical resistance: Resistance to the specific chemicals, solvents, and environmental conditions the pultruded parts will be exposed to. Thermal performance: Ability to withstand the operating temperatures and thermal cycling of the application. Processing characteristics: Viscosity, curing behavior, and other properties that enable efficient and consistent pultrusion production.
Other related products