-
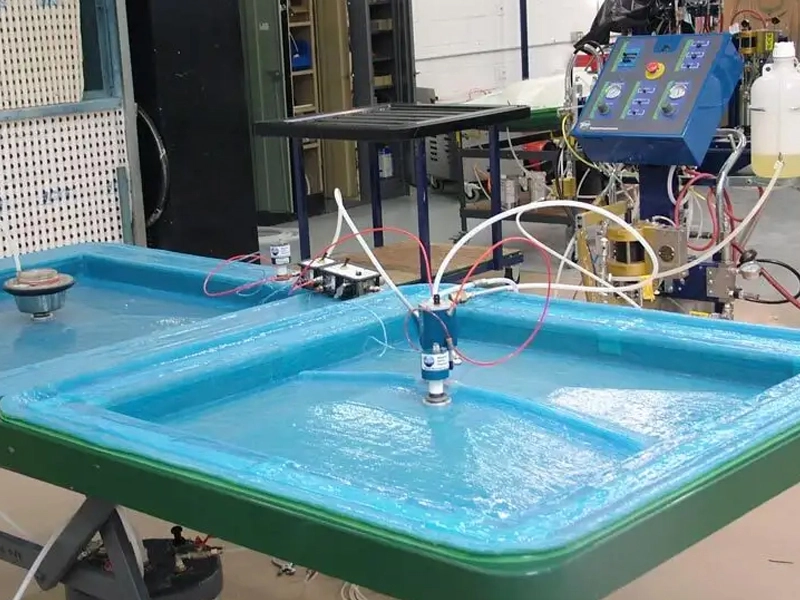
Vacuum/RTM Resin
-

Vacuum/RTM Resin
-

Vacuum/RTM Resin
-

Vacuum/RTM Resin
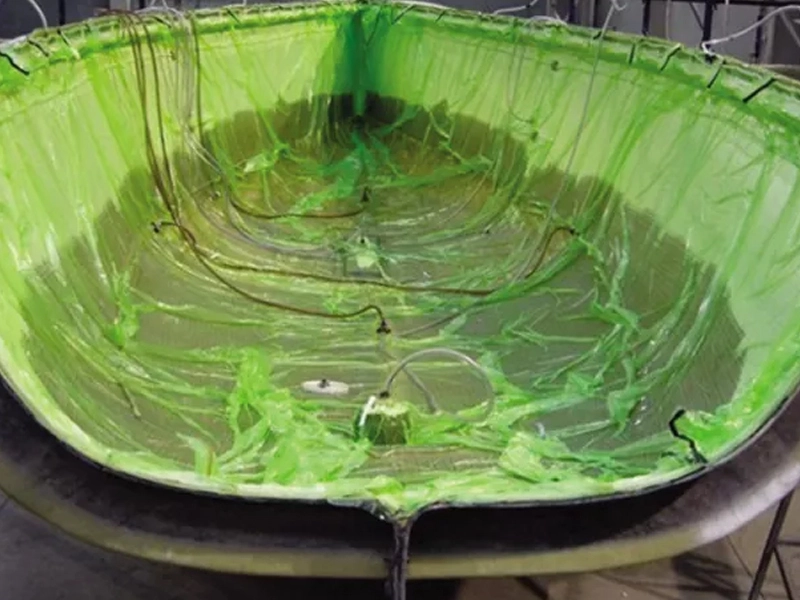
In closed-molding, raw materials (fibers and resin) cure inside a two-sided mold or within a vacuum bag (shut off from air).
Product performance introduction
Vacuum/RTM Resin refers to the type of thermosetting resin used in the vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) and resin transfer molding (RTM) composite manufacturing processes.
The key characteristics of Vacuum/RTM Resins include:
-
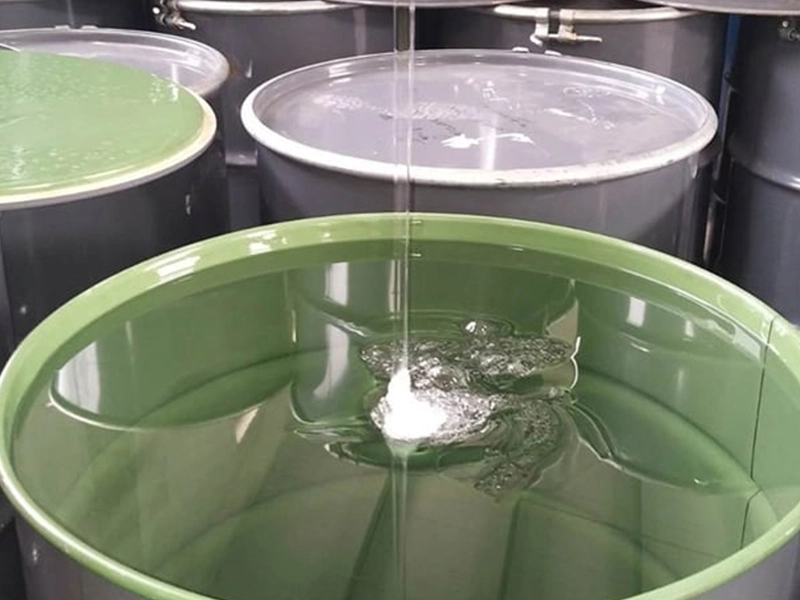
Low to Medium Viscosity:
- Typical viscosity range is 100-500 centipoises (cP).
- This low viscosity allows the resin to easily flow and impregnate the reinforcement fibers.
-
Compatibility with Reinforcements:
- The resin must be compatible with the reinforcement materials, such as glass, carbon, or aramid fibers.
- Good wetting and adhesion between the resin and fibers is important for mechanical performance.
-
Controlled Curing Behavior:
- The resin system includes catalysts, accelerators, and other additives to control the curing rate and extent of crosslinking.
- Proper curing ensures the desired mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of the composite.
-
Suitability for VARTM and RTM Processes:
- The resin viscosity and flow characteristics are tailored for effective impregnation under vacuum or injection pressure.
- Resins may be formulated to have a suitable pot life and cure time for the specific manufacturing process.
Common Vacuum/RTM Resin types include:
- Epoxy resins
- Polyester resins
- Vinyl ester resins
The selection of the appropriate Vacuum/RTM Resin depends on the specific requirements of the composite application, such as mechanical performance, environmental resistance, and manufacturing process parameters.
Here are the key points about the use of resin in vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) and resin transfer molding (RTM) processes:
Resin Selection:
- Common thermosetting resins used include epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester.
- Resin selection is based on desired mechanical properties, chemical resistance, curing characteristics, and compatibility with reinforcements.
- Low to medium viscosity resins (100-500 cP) are preferred for good impregnation.
Resin Preparation:
- Resins may require mixing with catalysts, accelerators, or other additives to control curing.
- Proper mixing and degassing is important to remove trapped air or volatiles.
Resin Injection and Impregnation:
- In VARTM, resin is drawn into the mold by vacuum, while in RTM it is actively injected under pressure.
- Resin flow and reinforcement impregnation are influenced by mold design, preform permeability, and injection parameters.
- The goal is to achieve complete and uniform resin impregnation without excessive resin flow or wastage.
Resin Curing:
- Curing parameters like temperature, time, and use of catalysts/accelerators are controlled.
- Proper curing ensures the desired degree of crosslinking and dimensional stability.
Defect Mitigation:
- Common defects include voids, dry spots, resin-rich/starved areas, and poor fiber-resin bonding.
- These can be minimized by optimizing resin viscosity, injection, and curing.
Resin Waste and Disposal:
- Unused resin, solvents, and other waste must be disposed of properly.
- Recycling and waste management practices help minimize environmental impact.
Safety Considerations:
- Appropriate PPE and ventilation are required when handling resins.
- Spill containment measures are important for worker and environmental safety.
Careful resin selection, preparation, and process control are crucial for producing high-quality composite parts using VARTM and RTM techniques.
tags:
Vacuum/RTM Resin
Series :
Unsaturated Polyester Resin >application
Aerospace,Automotive,Wind Energy,Marine,Infrastructure,Sports and Recreation
Brand name :
Vacuum/RTM Resin
FAQ
Q :
Why choose us?
A :
Professional service and competitive prices.
Other related products
-
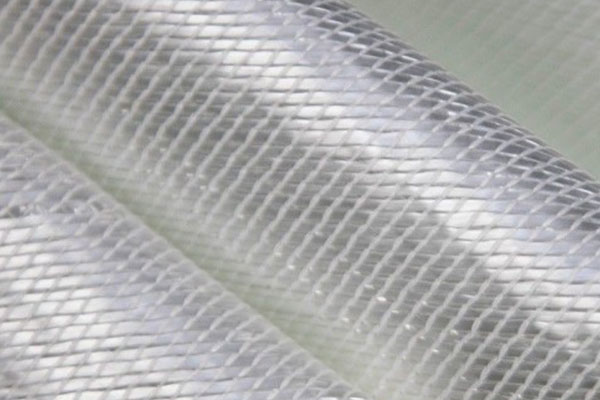

Glass Fiber Stitched Fabric
The stitching process not only holds the fibers together but also helps to distribute stresses more evenly across the fabric. As a result, stitched glass fiber fabrics offer superior mechanical pro...

-
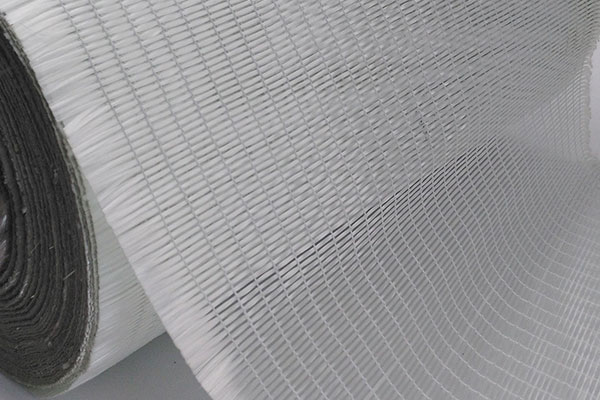

Glass Fiber Unidirectional Fabric
Unidirectional glass fiber fabric is most commonly used in applications requiring high tensile strength and low weight, such as aerospace, automotive, marine, and sports equipment industries. Its p...

-
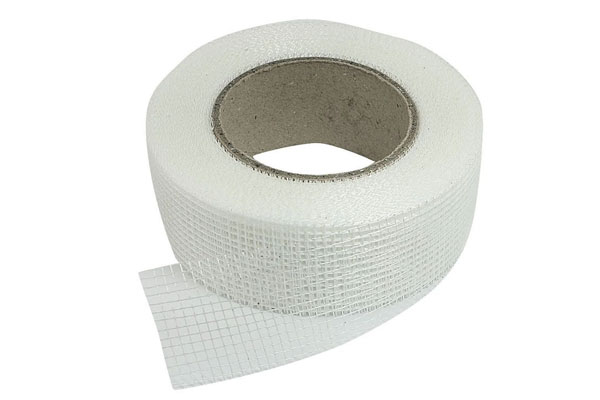

Fiberglass Tape
Fiberglass fabric is typically a woven textile composed of continuous filaments of glass fiber, which gives it remarkable strength and flexibility. It is available in different weave patterns (plai...

-
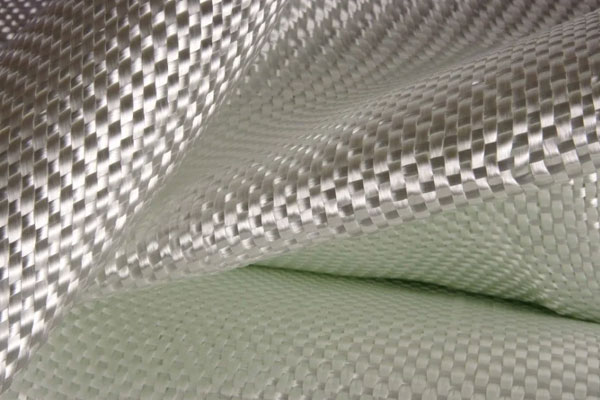

Glass Fiber Cloth
Glass fiber fabric is widely used in composite manufacturing, including in applications such as aerospace, automotive, marine, industrial, construction, and electrical insulation. It is known for i...

-
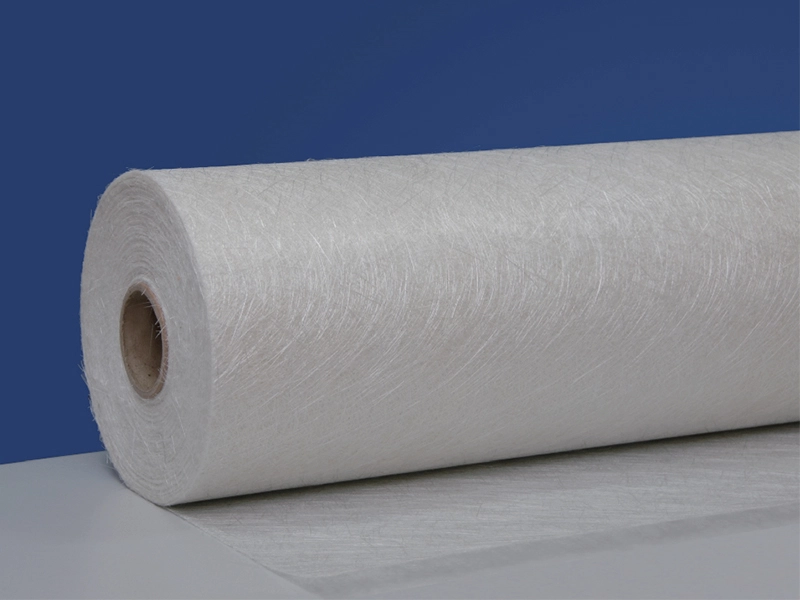

Glass Fiber Composite Mat
The glass fiber composite mat provides improved strength, durability, and flexibility in comparison to traditional chopped strand mats (CSM) or woven roving mats. It is engineered to meet the ne...

-

Glass Fiber Stitched Mat (Stitched Fiber Mat / Stitched Glass Fiber Mat)
This mat is binder-free, allowing for more efficient resin absorption, and faster and more uniform wet-out during molding processes. The use of stitching yarn also provides a more stable and dur...

-

Glass Fiber Stitched Felt (Stitched Mat / Stitched Nonwoven Felt)
The felt consists of randomly distributed fibers that are stitched in a grid-like pattern, which creates a more stable mat with increased dimensional integrity during molding and curing processes. ...

-

Glass Fiber Knitted Felt (Stitched Felt / Glass Fiber Nonwoven Mat)
Knitted felt is composed of short-length E-glass fibers (usually 50 mm or 100 mm) arranged in a random orientation and knitted in a lightweight, open-loop structure, providing uniform fiber distrib...

